When I first started using vacumetros in my lab, I was amazed at how they simplified our experiments. Monitoring vacuum levels became straightforward, allowing us to focus more on our research than on technical details. It’s been a game-changer for precision and efficiency in our work.
A vacumetros measures the level of vacuum pressure, which is important in fields such as science and industry. It helps maintain efficient operations by monitoring and controlling vacuum levels accurately.
This guide will explore the different types of vacumetros, their applications, and how they work in simple terms.
What Are Vacumetros?
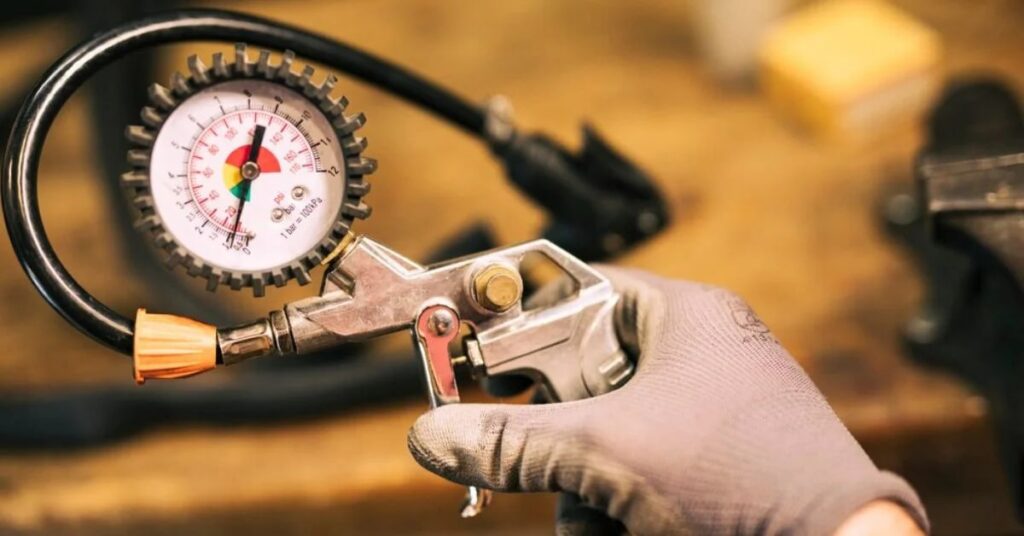

Vacumetros, also known as vacuum gauges, are tools used to measure the pressure inside a vacuum. Unlike typical gauges that measure normal (positive) pressure, vacumetros are specifically designed to measure low or negative pressure.
They are essential in many industries to monitor and control vacuum levels, ensuring that operations run efficiently and safely.
Types Of Vacumetros:
- Mechanical Vacumetros: These use parts like springs or diaphragms to measure vacuum pressure. They are straightforward and reliable for many basic applications.
- Electronic Vacumetros: These use sensors and electronic circuits to give precise measurements. They are commonly used in modern and high-tech applications due to their accuracy.
- Thermocouple Vacumetros: These measure vacuum levels by detecting temperature changes in a heated wire or filament. They are often used in scientific and industrial settings where precise vacuum measurement is needed.
How Do Vacumetros Work?
Vacumetros operate on principles that allow them to sense and display the pressure within a vacuum system. Depending on the type, they might use mechanical deflection, changes in electrical resistance, or thermal conductivity to provide readings.
The measurement is usually displayed on a dial or a digital screen, allowing users to monitor and control vacuum levels effectively.
Applications of Vacumetros:
1. Automotive Industry:
In cars and trucks, vacumetros help check the vacuum pressure in engines. Mechanics use them to spot problems like leaks or performance issues in parts like the intake manifold. By monitoring vacuum pressure, they can make sure engines run smoothly and efficiently, improving vehicle performance.
2. Scientific Research:
In labs, vacumetros are crucial for experiments that require controlled vacuum conditions. They are used in vacuum chambers for experiments in physics and chemistry. Precise vacuum control is necessary to ensure accurate experimental results.
3. Manufacturing Processes:
In manufacturing, vacumetros play a key role in processes like vacuum packaging. This process seals products in airtight conditions, which is essential for maintaining product quality and extending shelf life. Vacumetros help keep the vacuum levels just right during these processes.
4. HVAC Systems:
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems use vacumetros to control and monitor vacuum pressure. Proper vacuum levels are important to ensure that air is circulated and filtered correctly, maintaining a comfortable and safe indoor environment.
5. Medical Applications:
In the medical field, vacumetros are used in devices like vacuum pumps and autoclaves. These devices need precise vacuum levels to work properly. For example, vacumetros help ensure effective sterilization in autoclaves and provide necessary suction during surgeries.
By maintaining the correct vacuum pressure, vacumetros help ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability in various applications.
How To Use A Vacumetros?
- Connect the Vacumetro: Attach the vacumetro securely to the part of the vacuum system where pressure needs to be measured.
- Calibrate if Needed: Some vacumetros require calibration before use. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate readings.
- Read the Measurement: Check the vacumetro display for the vacuum pressure reading. Analog gauges show a needle position, while digital gauges display numerical values.
- Understand the Results: Compare the vacuum pressure reading with the desired range for your application to ensure optimal performance.
- Adjust as Needed: If the vacuum pressure is outside the desired range, make necessary adjustments to the system to achieve the correct pressure level.
How To Choose The Right Vacumetros?
1. Measurement Range:
Different vacumetros measure different levels of vacuum. Ensure the one you choose can handle the vacuum levels required for your application. For instance, high-vacuum applications need gauges that measure very low pressures.
2. Accuracy:
Precision is crucial, especially in scientific research and critical industries. Opt for vacumetros that provide high accuracy with minimal errors to ensure reliable measurements.
3. Durability:
Consider where and how the vacumetro will be used. Industrial settings require gauges that are durable and resistant to harsh conditions. Look for models made from sturdy materials that can withstand rough handling.
4. Type of Display:
Vacumetros offer either analog or digital displays. Analog displays are straightforward and easy to interpret, while digital displays provide precise numerical readings. Choose the display type that best suits your preferences and application requirements.
Maintenance And Troubleshooting:
1. Regular Calibration:
Calibration ensures that your vacumetro provides accurate readings. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for calibration intervals and procedures. Use calibration tools or services recommended by the manufacturer to maintain precision.
2. Keep it Clean:
Cleanliness is crucial for vacumetros, especially mechanical ones that use delicate components. Use a soft, dry cloth to wipe down the gauge regularly, removing any dust or debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage sensitive parts.
3. Check for Leaks:
Vacuum leaks can compromise the accuracy of your vacumetro’s readings. Conduct periodic leak tests on your vacuum system using a suitable leak detection method. Fix any leaks promptly by tightening fittings, replacing seals, or repairing damaged components to ensure consistent and reliable measurements.
What Are The Troubleshooting Common Issues?
- Inconsistent Readings: If the vacumetro gives fluctuating or inconsistent readings, check for leaks or ensure it is properly connected.
- No Display on Digital Gauges: If a digital vacumetro is not displaying anything, check the power supply or batteries.
- Stuck Needle on Analog Gauges: For analog vacumetros, a stuck needle may indicate internal damage or the need for recalibration.
Innovations In Vacumetro Technology:

1. Wireless Connectivity:
Some vacumetros now offer wireless connectivity, allowing remote monitoring and data logging. This is particularly useful in industrial applications where continuous monitoring is required.
2. Integration with Control Systems:
Advanced vacumetros can be integrated with automated control systems. This allows for automatic adjustments to vacuum levels based on real-time measurements, enhancing efficiency and precision.
3. Enhanced Sensitivity:
Newer vacumetros provide enhanced sensitivity, capable of detecting even the slightest changes in vacuum pressure. This is critical in applications requiring high precision.
FAQ’s:
1. What is the unit of a vacuum?
In simple terms, the unit used to measure vacuum gas pressure is called the pascal (Pa). Other common units for measuring vacuum include torr, micron, and mbar.
2. Are vacumetros easy to use?
Yes, vacumetros are designed to be user-friendly, with straightforward steps for connecting, reading, and interpreting vacuum pressure.
3. Can vacumetros measure both low and high vacuum levels?
Yes, depending on the type, vacumetros can measure both low and high vacuum levels accurately.
4. Can vacumetros be used in portable applications?
Yes, there are portable vacumetros available for applications where mobility and ease of use are important.
Conclusion:
Vacumetros are essential devices used across industries like automotive and scientific research for precise vacuum measurements. Knowing their types, applications, and effective selection and usage is key for accuracy.
With advancing technology, vacumetros now provide better precision and enhanced features for improved performance.








